Attribute Mapping
Overview
When integrating with your Identity Provider (IdP), ShellHub needs to identify and authenticate users based on specific attributes in the SAML assertion. The most crucial requirement is a unique and persistent identifier in the NameID field, which could be a persistent ID or any other attribute that consistently identifies users within your IdP, followed by a email and a display name.
Required Attributes
ShellHub requires two fundamental attributes for successful authentication:
- The user's email address, which by default is retrieved from the
emailaddressattribute in your SAML assertion. This serves as the primary identifier for the user within ShellHub. - The user's display name, which ShellHub looks for in the
displaynameattribute by default. This name is used throughout the interface to identify the user.
Customizing Attribute Mapping
While ShellHub provides default mappings, you can customize which IdP attributes should be used for authentication.
For example, if your IdP uses email instead of emailaddress, you can
configure ShellHub to look for the email attribute there instead.
You can configure custom mappings through your IdP configuration settings in the "Advanced Settings" section under "SAML Mappings". The "ADD MAPPING" button allows you to create new mappings, where the left field shows the ShellHub attribute and the right input specifies your IdP's corresponding attribute name.
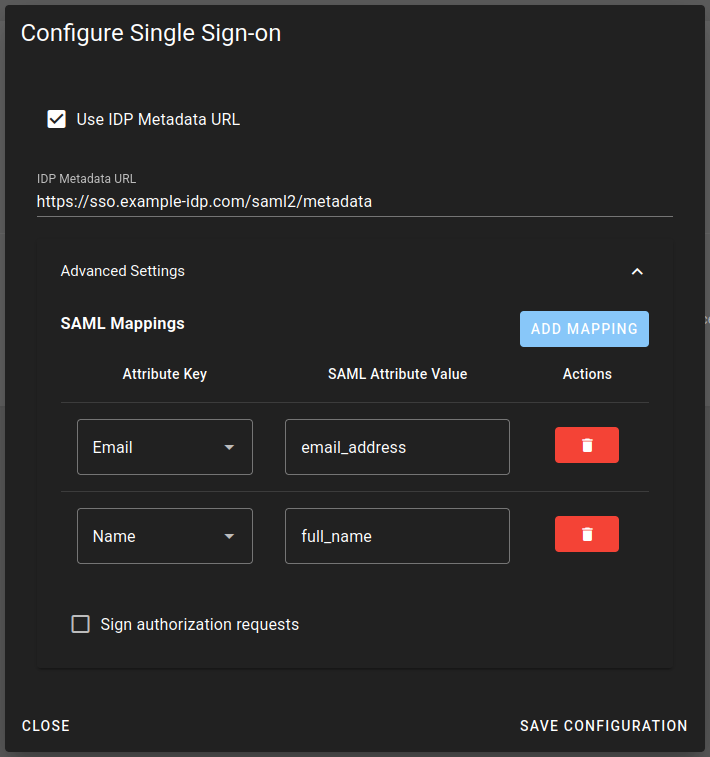
Attribute mapping is case-insensitive. For example, emailAddress,
emailaddress, and EMAILADDRESS are all treated the same way.
Error Handling
Authentication will fail with a 400 Bad Request status code if either
required attribute is missing from the SAML assertion. ShellHub performs these
validation checks before processing the authentication request to ensure data
integrity.
In these cases, the user will be redirected back to the login page and an error message will be displayed showing the missing attributes, as shown in the image below:
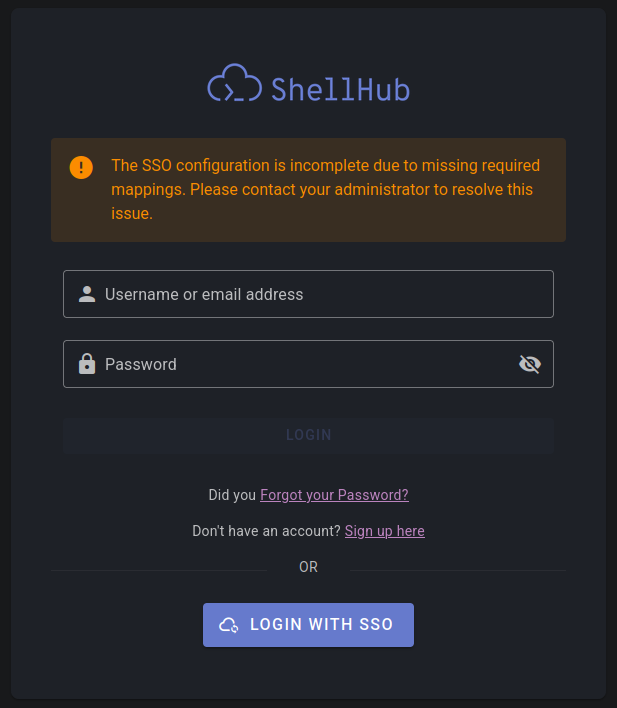
You can identify the specific missing attributes by checking the URL's
missing_assertions query parameter. For example:
?missing_assertions=emailaddress,displayname